Credit Policy Automation: Streamlining Risk Decisions in Real Time
Sofia Rangoni

Jan 23, 2026

What Is Credit Policy Automation?
Credit policy automation is the practice of translating a company's lending and risk guidelines into a digital process: one that assesses applications, scores risk, and makes decisions without reliance on slow, manual review. Instead of a loan officer rummaging through spreadsheets and documents to decide if a customer deserves credit, automation handles much of the work behind the scenes almost instantly.
Manual vs Automated Credit Policies
Before automation, credit decisioning meant wading through paper trails, cross-checking references, and waiting days, or even weeks, for verdicts. Human oversight at every step led to inconsistency, delays, and a higher risk of overlook errors or subjective judgments. By comparison, automated credit policies use pre-set rules to analyze applicant data, request additional information if needed, and reach an answer in seconds. Decisions are based on consistent criteria and can be easily tracked and audited. This reduces the churn and friction that manual processing inevitably causes.
How Automation Fits Into the Credit Cycle
Automation isn’t just about rapid decisions when an application is submitted. It extends across the entire credit lifecycle: evaluating new prospects, adjusting lines of credit as businesses change, and monitoring for early warning signals of risk. With an automated approach, updates to credit policy can be pushed live instantly, and adjustments for market shifts or regulatory changes are just one rule update away. This enables a business to be both nimble and scalable in how it controls risk exposure.
Understanding what automation looks like in action is only the first step: next, let’s explore why leading companies are investing in these capabilities and what strategic advantages they unlock in the real world.
Why Modern Businesses Automate Credit Policies
Reducing Manual Errors and Bias
Even the most meticulous credit analysts aren’t immune to oversights. Manual credit reviews leave room for accidental miscalculations or missed red flags, especially when workloads spike. Human decisions can also be swayed by unconscious bias, leading to unfair approval patterns or unintended risk concentrations. Automation replaces ambiguity with precise rule application, every application is reviewed consistently, and every decision is backed by transparent data points. This approach not only sharpens risk controls but also supports compliance with increasingly stringent fair lending regulations.
Speeding Up Credit Decisions without Risking Control
Customers and partners now expect real-time responses, whether they're applying for B2B terms or a personal instalment plan. Manual reviews lead to delays, sometimes hours, sometimes days, while applications languish in inboxes or shuffle between departments. Automated credit policy engines process applications within seconds, scoring risk and triggering next steps instantly. Crucially, this doesn’t mean sacrificing risk discipline: well-designed automation checks every application against updated policies and flags cases that need extra scrutiny, blending responsiveness with security.
As more businesses recognise the limits of manual reviews, the question shifts from “why automate” to “how to build a system that works.” Next, we’ll pull back the curtain on the components that make credit policy automation both reliable and adaptable.
Key Components of Effective Credit Policy Automation
Core Data Sources and Integrations
At the heart of any automated credit policy lies robust connectivity to relevant data. This usually includes live feeds from credit bureaus, internal transaction histories, third-party risk databases, and sometimes even alternative signals, like utility payment records or e-commerce activity. Integrating these sources directly into the decision engine ensures that every risk assessment draws from the freshest, most complete information possible.
Custom Scoring Models and Segmentation
One-size-fits-all scoring quickly becomes a limitation in dynamic environments. Effective automation uses tailored scoring models designed around the unique attributes and behaviors of your customer base. Granular segmentation, by product, location, customer type, or risk profile, allows policies to adapt instantly to meaningful differences, preserving precision even at scale.
Approval Workflows and Exception Handling
Automation thrives with clear decision pathways, but there are always edge cases. Effective systems embed granular approval workflows, automatically routing straightforward applications for instant decisions, while flagging complex or borderline cases for further review. Built-in exception handling ensures no scenario falls through the cracks, balancing efficiency with necessary scrutiny.
Alerts and Early Warning Triggers
Real-time alerts catch shifting risk long before it results in loss. Automated policies can send notifications based on sudden changes in payment behavior, unexpected industry signals, or deviations from typical patterns. Early warnings empower teams to intervene and adjust limits or terms proactively, reducing both surprises and downstream losses.
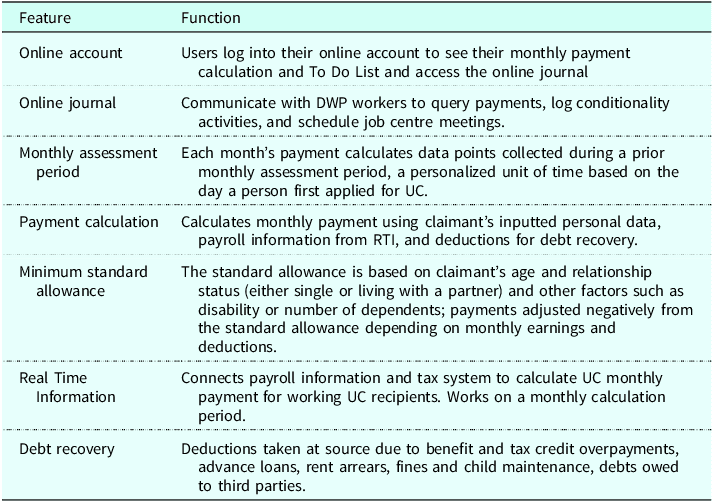
Monitoring Dashboards
Continuous insight is essential in automation. Monitoring dashboards track approval rates, overrides, delinquency, portfolio risk metrics, and more, often in a single unified view. They enable credit teams to spot trends, audit policy performance, and quickly troubleshoot bottlenecks or anomalies.
The chart shows key performance indicators and metrics used in monitoring dashboards for credit policy automation, sourced from Cambridge.
With these components working together, automation moves beyond speed, becoming a tool for insight and risk control. The next stage is knowing how to set up these elements for your business and keep them aligned as your environment changes.
How To Set Up and Refine Automated Credit Policies
Mapping Business Rules to Automation Logic
The first step is translating your company’s unique credit criteria into precise, actionable rules. Start by identifying the specific conditions that have defined approval, rejection, or review decisions in your manual processes, factors like payment history, outstanding balances, and customer segmentation based on risk score.
Each business rule should be broken down into logical statements that software can understand. This might look like: “If a customer has two or more late payments in 12 months, reduce credit limit,” or “Approve instantly if internal risk score is above 85 and no overdue invoices exist.” Assemble these conditions in your automation platform, using decision trees or script-based engines to replicate human judgment, minus the inconsistency.
Collaboration with credit analysts is crucial during this mapping phase. Their practical experience helps ensure no vital nuance gets lost in translation. Document every rule and its rationale so updates or audits later aren’t a guessing game.
Testing, Rollout, and Continuous Improvement
Before going live, test your automated policies on historical data. This “sandbox mode” lets you see how your new logic would have handled past decisions: Did it catch all high-risk accounts? Would it have inadvertently restricted credit for top customers? Validate results with stakeholders, adjusting thresholds and logic where outcomes don’t match intent.
Once performance looks solid, pilot the system on a small segment, such as new applicants or a low-risk customer group. Monitor every decision, track exceptions, and collect feedback from users interacting with the automated process. This controlled rollout allows you to spot and fix edge-case errors before a wider launch.
Automation isn’t a “set and forget” affair. Build feedback loops to refine your policy: Review decisions weekly, analyze override patterns, and solicit regular input from risk teams. As market conditions evolve, so should your rules. The goal is a living system that adapts swiftly, keeps policies aligned with business goals, and continuously learns from real-world outcomes.
Mastering these setup and refinement steps is essential for unleashing the true value of policy automation. The next challenge, however, lies in managing what happens when the rules don’t quite fit, especially when human judgment needs to intervene.
Handling Overrides and Special Cases
Override Approval Processes
As powerful as credit policy automation is, there are always exceptions, cases where a customer doesn’t fit the usual risk profile, or where business relationships justify looking beyond the standard scoring. This is where override mechanisms come into play. An effective system routes override requests directly to authorized decision-makers, requiring a clear justification before any deviation from the automated rules. For example, a manual override might be needed for a long-standing client who temporarily dips below a credit threshold due to a one-off event. Here, the override flow should be auditable and logged, not handled through off-system email threads or phone calls.
Documenting Rationale and Maintaining Transparency
Every override creates a trail of who approved it, why, and on what basis. Modern automation platforms not only capture this data, but they also provide structured fields for rationale, attach supporting documents, and timestamp every step. This documentation is crucial for internal audits and regulatory reviews. It also discourages arbitrary exceptions by forcing users to think critically about their justifications, ensuring each special case truly merits an exception. Transparent recordkeeping builds confidence across audit, compliance, and business teams.
Establishing robust override protocols strengthens automated credit policies. With the right checks in place, your team can address edge cases confidently, without undermining the system’s integrity. Up next, learn how to nurture long-term trust in your automation process and keep it ready for tomorrow’s challenges.
Best Practices for Sustainable Automation
Tracking Key Metrics
A robust credit policy automation system is only as strong as the feedback you mine from its data. Focus on metrics beyond approval rates, delve into delinquency trends and near-miss cases, where the system correctly prevented risky approvals. Regularly analyze adverse actions resulting from automated decisions to spot false positives. Compare real-time outcomes with historical benchmarks so you spot process drift early, not months after it damages your portfolio.
Training Teams to Trust Automated Policies
Even the smartest algorithms collapse when ignored. Bring operations and risk management teams into the process early, explain not just what the system does, but how it’s built and why certain rules exist. Regular sessions where teams review anonymized edge cases can replace skepticism with healthy vigilance. Encourage teams to surface exceptions they don’t understand, so feedback triggers continuous improvement rather than silent workarounds.
Dealing with Alert Fatigue and Keeping the System Relevant
Bombarding analysts with redundant alerts breeds apathy. Audit your alert system quarterly, pruning triggers that no longer signal real risk. Introduce graduated notifications, where the system distinguishes urgent action from informational updates. Refresh automation rules regularly in response to market changes or internal policy shifts: an outdated model is riskier than none at all.
Building a reliable and responsive automation system calls for discipline and dialogue, qualities that also help navigate common hurdles and pitfalls, which deserve a closer look next.
Common Challenges and How to Address Them
Outdated Data Inputs
Inaccurate or stale data often slips into automated credit systems, warping decisions and inflating risk. Real-time data sources, like APIs feeding credit bureaus or transaction feeds, can help. Set automated refresh schedules or validation steps to flag suspiciously old records. Human spot checks periodically validate that the data pipeline hasn’t gone awry.
Override Overuse
When teams frequently bypass automated recommendations, the system loses credibility. Pattern analysis can pinpoint the parts of policy logic that invite manual intervention, often because rules are too rigid or miss key nuances. Use override tracking to surface common exceptions, then refine scoring criteria or add new data sources to handle edge cases automatically, tightening loopholes without handcuffing reviewers.
System Integration Roadblocks
Disparate platforms rarely play nice from the start; batch file uploads, ad-hoc spreadsheets, or copy-paste hacks may linger. Focus first on building dependable bridges between core systems, such as CRM, ERP, and risk models, using standardized APIs or secure ETL tools. Automate health checks to spot outages fast. Bring tech and business teams together early, before relying on the automation for high-stakes decisions.
When these challenges are met head-on, automation doesn’t just run, it adapts and improves. Next, let's see what’s on the horizon for credit policy technology and how these advancements promise smarter, faster decisions for tomorrow's businesses.
Future Trends: AI and Machine Learning in Credit Policy Automation
The boundaries of credit policy automation are expanding rapidly thanks to AI and machine learning. Traditional rule-based engines, while effective at enforcing static business logic, struggle to keep up with shifting risk patterns, emerging fraud tactics, and evolving customer profiles. AI-powered systems don't just follow pre-set rules; they learn from new data, spot subtle patterns, and adapt in near real time.
One practical example is the use of machine learning algorithms to enhance credit scoring. These models ingest thousands of data points, from payment histories and transaction patterns to alternative signals like digital footprint or behavioral biometrics. The result is a risk assessment that becomes sharper over time, not duller, a moving target that stays locked on emerging risks before they materialize on a loss statement.
AI also pushes automation deeper into decisioning workflows. Natural language processing is making it possible to ingest unstructured data, such as emails or public filings, reducing reliance on structured feeds alone. Meanwhile, anomaly detection algorithms track accounts for early warning signals, like sudden changes in payment habits or suspicious behavioral spikes, enabling proactive interventions instead of reactive crisis management.
Explainability remains a top priority. Regulations and internal policies require that credit decisions can be understood and defended. Cutting-edge AI platforms now prioritize "glass box" transparency, surfacing the key drivers behind individual credit decisions and highlighting how a model's recommendations align with policy requirements.
As these trends accelerate, getting the most out of AI and machine learning means choosing wisely, balancing innovation with security, automation with oversight, and accuracy with fairness. The landscape is rapidly evolving, but those who embrace these tools will keep their credit decisioning sharp, adaptive, and resilient.
But theory is only one side of the equation. Next, let’s look at real companies that put these innovations into practice, uncovering lessons from success stories, and missteps, that can accelerate your own automation journey.
Real-World Examples: Automation in Action
Industry-Specific Solutions
In retail banking, instant credit decision platforms review an applicant’s financial data, spending patterns, and credit bureau reports within seconds. For example, a leading online lender reduced manual checks by integrating bank transaction feeds with automated rule-based engines. This cut approval times from days to minutes and lowered default rates by flagging anomalies early.
In B2B manufacturing, suppliers use automation to tailor credit terms by customer segment. A global supplier built a system that dynamically adjusts credit limits based on real-time payment behavior and order size. As a result, their DSO (days sales outstanding) dropped by nearly 18% within six months, and they could tap into lucrative customers previously overlooked by risk-averse manual reviews.
Lessons Learned from Failed Implementations
One fintech startup overlooked data quality checks when automating customer onboarding. Incorrect feeds led to several low-risk applicants being wrongly declined, triggering a surge in complaints and regulatory scrutiny. After reverting to a semi-automated flow and tightening their data validations, they rebuilt trust and compliance.
In another case, a logistics firm rushed to replace legacy risk scoring models with an off-the-shelf automation engine. Without ongoing monitoring and team training, overrides ballooned, and exception queues became unmanageable. Only after investing in better alerts and staff education did they see improvement.
These examples highlight why context matters, success depends on matching the automation approach to business realities, not just plugging technology into existing workflows.
With this foundation, let’s explore practical steps to set up and continuously refine your own automated credit policies for resilient decision-making.
FAQ: Credit Policy Automation Essentials
How do you automate credit limits for new customers?
Credit limits for new applicants can be automated by integrating real-time data sources, such as credit bureaus, payment history, and internal transaction behavior, into your decision engine. Automated systems run these inputs through custom scoring models, mapping business rules to set responsible initial limits. Continuous monitoring then allows for rapid limit adjustments as each customer’s risk profile evolves.
What controls ensure automation doesn’t go unchecked?
Precise rule configuration is key, but oversight doesn’t end with deployment. Automated workflows often include built-in escalation paths for edge-case reviews, regular audit trails, and alerting for outlier approvals. Routine checks by credit managers further ensure the automation remains aligned with business goals and regulatory requirements.
How can automation adapt to regulatory changes?
Modern automation tools are built for flexibility. When regulations shift, you can update rule sets and scoring triggers without rewriting the entire workflow. Many platforms support versioning, so you can test, review, and roll back changes if needed, keeping your compliance agile as the landscape evolves.
Understanding core automation practices prepares you for the practical steps of designing and refining your own credit policies, where a structured approach makes all the difference.
Related posts
Ready To Join The Circular Movement?
United for a smarter shopping experience and a better planet